
Eczema of the lips is a condition in which blisters and redness appear on the lips, causing peeling. The symptoms of the disease are often easily confused with the common condition of dry lips, causing patients to be subjective and not have early treatment measures. So what causes eczema of the lips? How should we handle it when we detect the initial signs of the disease?
What is lip eczema and what are the types?
Eczema of the lips or eczematous cheilitis is a common dermatological disease in all ages. The disease is characterized by typical symptoms such as small blisters, red burning on the lips, then the blisters burst, secrete fluid, and finally form scabs and peel. Eczema of the lips can come from many causes, including endogenous and exogenous factors.
Similar to eczema in other parts of the body, lip eczema also progresses through different stages. The disease often tends to be persistent and recur many times if not treated properly. Although it does not directly threaten the patient’s health, lip eczema still causes discomfort, psychological fear and lack of confidence in daily communication. So what types of lip eczema should you pay attention to?
According to dermatologists, lip eczema can be divided into the following 3 distinct types:
- Contact cheilitis: This type of eczema often occurs when the lips come into direct contact with chemicals in cosmetics, are affected by weather or sunlight causing irritation. These factors cause dry lips and reduce immunity leading to inflammation.
- Allergic contact cheilitis : Symptoms of this type of lip eczema often flare up when the skin of the lips comes into contact with allergenic ingredients in toothpaste, lipstick or medicine, etc.
- Exfoliative cheilitis: This is one of the most common forms of lip eczema, characterized by flaking and scaling of the lips. The disease is often spontaneous and the cause is difficult to determine, and it is very easy to recur many times.
What are the causes of lip eczema?
The cause of lip eczema is certainly the primary concern of patients when they first discover symptoms. Determining the cause of the disease will help you have the right treatment and management method. According to experts, lip eczema can originate from the following endogenous and exogenous factors.
Endogenous causes of cheilitis:
- Genetic factors: According to research, if a family member has a history of skin diseases such as atopic dermatitis , asthma, or allergic rhinitis, your risk of developing the disease will also be higher.
- Hormone imbalance : Hormone imbalance or abnormal changes in hormones during puberty, after pregnancy and menopause can facilitate the flare-up of eczema symptoms.
- Stress: Psychological stress, frequent pressure and fatigue in daily life are the causes of zinc, iron or B vitamin deficiencies, causing dry lips and eczema. Therefore, when your nervous system is under a lot of stress, lip eczema will also flare up and spread more easily.
- Respiratory tract infections: When you have respiratory diseases such as flu, colds, etc., your immune system will also weaken and be more sensitive than normal, creating conditions for symptoms to appear.
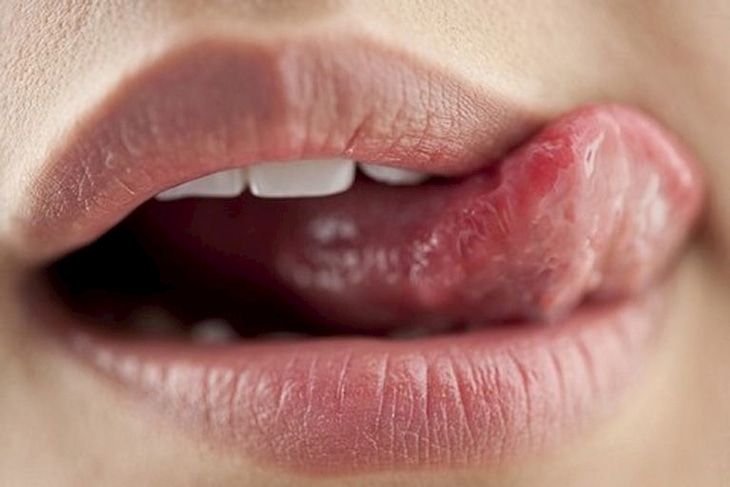

Besides endogenous causes, lip eczema can also originate from some exogenous factors such as:
- The habit of licking lips makes the skin of the lips dry and susceptible to infection.
- Allergic to lip tattoo, lipstick and other cosmetics.
- Allergic reaction to perfumes, shampoos, shower gels, soaps and other detergents when accidentally exposed to the lips.
- Allergy to fabrics and certain foods such as seafood, milk and animal milk products.
- Previous damage to the skin of the lips and around the mouth that is not properly cared for can lead to infection and cause lip eczema.
- Weather changes and sudden cold climates cause self-production of antigens and outbreaks of eczema symptoms on the lips.
Symptoms of the disease and how to recognize it
Symptoms of eczema can appear on both the upper and lower lips, but they can easily be confused with the common condition of dry lips. Therefore, patients need to understand the following basic signs to have timely treatment.
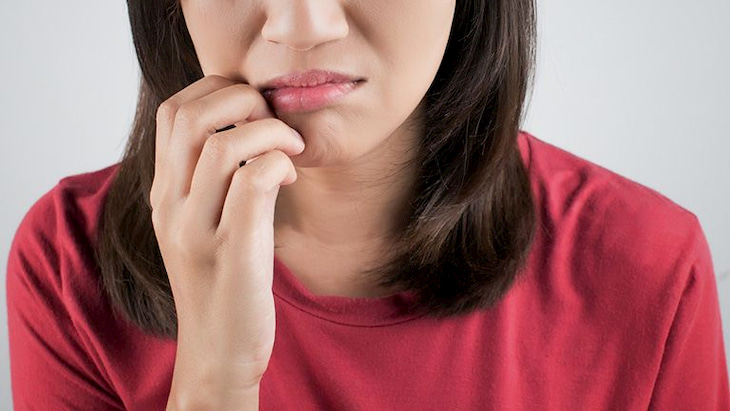

- The skin of the lips and the skin around the mouth shows signs of unusual redness.
- Initially, the lips will appear itchy and dry, then gradually form cracks on the lips, the skin peels off in large patches, making the lips dark and the patient has difficulty eating and drinking.
- Over time, the itching and pain will increase, and small, red blisters will begin to appear around the lip line. These blisters can burst and secrete fluid, forming ulcers that eat deep into the skin.
- The longer the eczema is left, the more it will spread, causing ulcers and making the patient feel stiff and swollen lips.
- In some cases, symptoms may appear intermittently, alternating with periods of remission.
Eczema of the lips is not only persistent and easy to relapse, causing a lot of pain and hindering the daily life of the patient. However, many people still have a subjective mentality, do not have an early treatment method, this can increase the risk of secondary infection and infection of the lips.
How to treat lip eczema effectively and safely
Based on clinical symptoms as well as family medical history, doctors will make an initial diagnosis of the level of inflammation caused by lip eczema. Then, the patient will be asked to perform a number of Patch Tests with suspected allergens to determine the cause.
From the results obtained, doctors will give the most appropriate treatment methods for the patient’s condition.
How to treat lip eczema with Western medicine
Using Western medicine to treat eczema is the fastest way to treat the disease, suitable for cases of severe pain, itching and serious inflammation. Below are some of the most commonly used oral and topical medications to treat lip eczema today.
- H1 antihistamines: These are drugs that can inhibit histamine mediators, helping to limit allergic reactions and reduce itching and burning symptoms caused by lip eczema.
- Topical Corticoids: Topical medications containing Corticoids have anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic effects. You can apply the medication directly to the eczema-affected skin areas at least twice a day, continuously for 2 weeks to quickly reduce the symptoms of the disease. However, you should also be aware of some side effects of the medication such as thinning of the skin and dilated capillaries.
- Calcineurin inhibitors: These drugs are often prescribed when topical corticosteroids are no longer effective. This group of drugs has similar effects to corticosteroids but is more potent and causes fewer side effects.
- Antifungal and antibiotic drugs: For patients with lip eczema at high risk of secondary infection, mainly due to the invasion of bacteria and fungi, doctors will prescribe treatment with these drugs.
Folk tips to treat lip eczema at home
The skin of the lips is often thin and quite sensitive, easily irritated by topical medications. Therefore, if the symptoms of lip eczema are only mild, you can proactively overcome them by moisturizing and applying some folk remedies to treat eczema below.
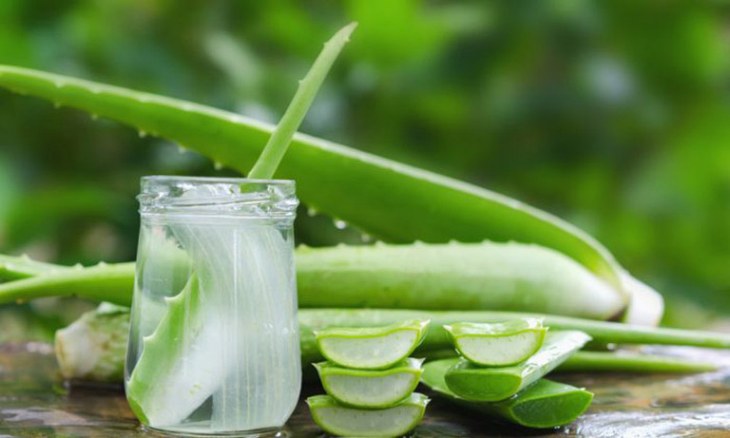

- Treating lip eczema with coconut oil: Coconut oil is a natural solution with a high content of fatty acids, which is very useful in soothing and moisturizing the skin. The active ingredients in coconut oil will also help strengthen the protective barrier of the lips, inhibiting the activity of Candida fungi and staphylococci. Thereby quickly reducing the symptoms of lip eczema and preventing the risk of secondary infection.
- Use aloe vera gel: Aloe vera has the effect of moisturizing and soothing the skin safely. Therefore, you just need to apply a thin layer of aloe vera on the skin with eczema on the lips, leave it for 15 minutes and then rinse with clean water every day.
- Treating lip eczema with betel leaves : Betel leaves have antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties, often used in remedies for skin diseases, especially lip eczema. Use a few fresh betel leaves, wash them and let them drain. Then put them in a mortar and crush them and squeeze out the juice, use a cotton swab to absorb the juice and gently apply it to the skin. Wait 30 minutes then rinse with clean water, apply this method 2-3 times/week to see clear results.
Proactive measures to prevent disease
Eczema is a common disease in all ages. Although it does not directly affect the patient’s health, eczema still causes a lot of inconvenience, hindering communication in daily life. There is even a risk of eczema infection , creating opportunities for bacteria and viruses to enter the body. Therefore, you should proactively prevent this disease early, avoid waiting until the symptoms have become serious, lasting for a long time before finding a way to fix it.
Along with treatments for lip eczema, patients also need to change their body care and diet to increase the effectiveness of the medication. Specifically, people with eczema-induced lip inflammation should note the following:
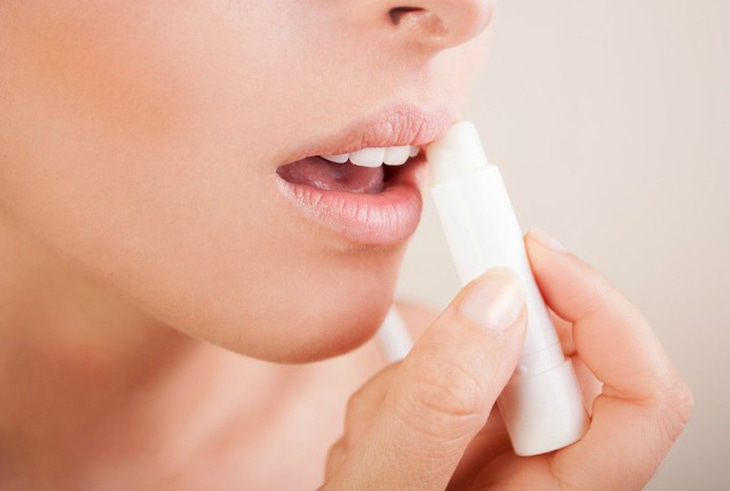

- Absolutely do not use your hands to rub your lips and limit licking your lips, because these habits can make your lips drier and more chapped.
- The most important thing to prevent eczema is to moisturize your lips regularly. You can use some folk remedies or lip balms to keep your lips moist. Consult a dermatologist for advice on using suitable lip care products.
- Limit foods that can cause irritation such as seafood, peanuts, wheat, do not smoke and stay away from cigarette smoke.
- Clean your face and lips regularly, get enough sleep and don’t stay up too late to naturally weaken your immune system.
- Focus on thoroughly treating respiratory infections right from the start.
Above is basic information about lip eczema and effective treatment. Lip eczema is a common skin disease in both children and adults. The disease only causes skin lesions, but can progress to a stage of secondary infection or infection, leading to many consequences. Therefore, patients should absolutely not be subjective, and need to take measures to overcome and treat it early.